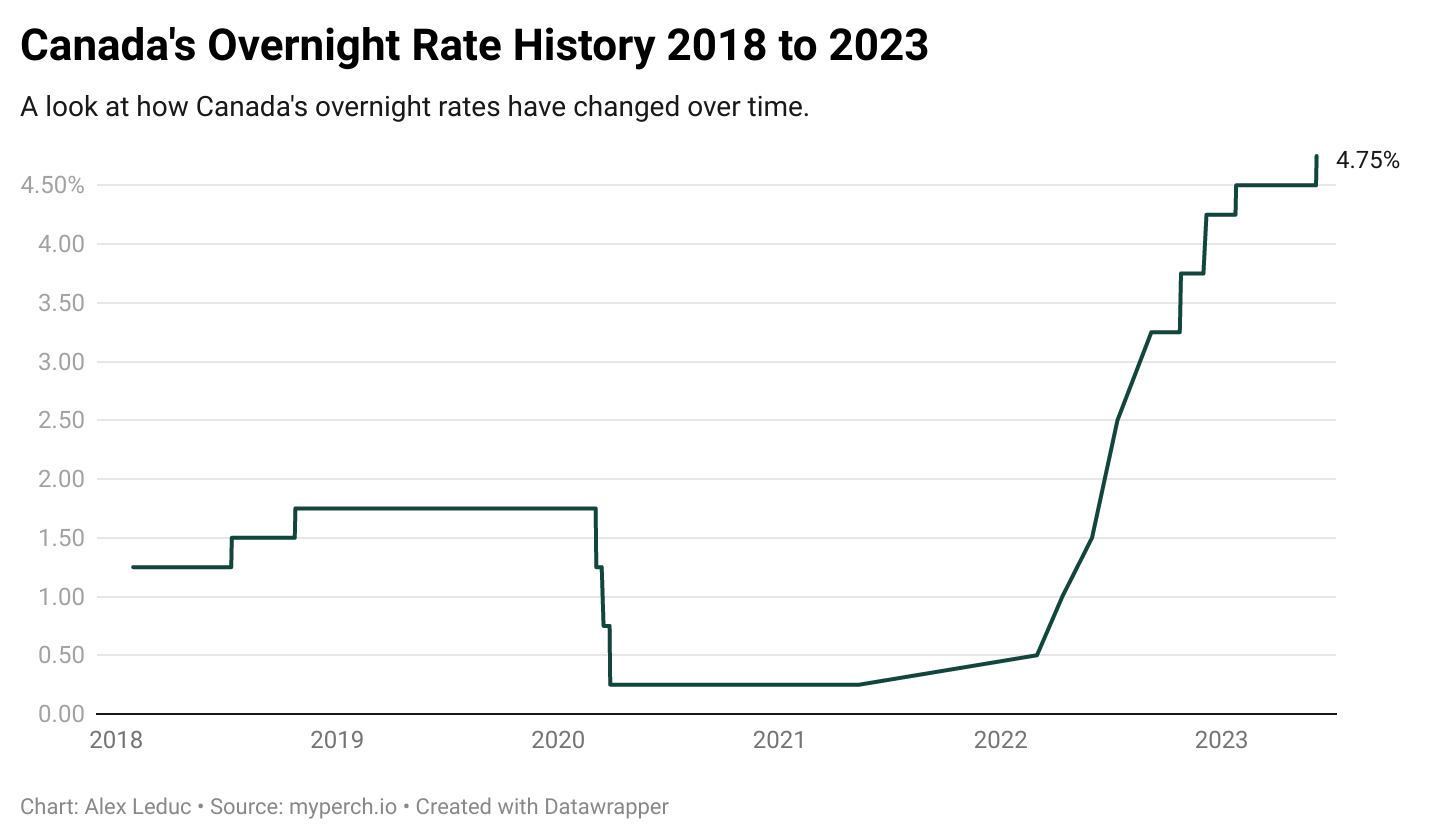
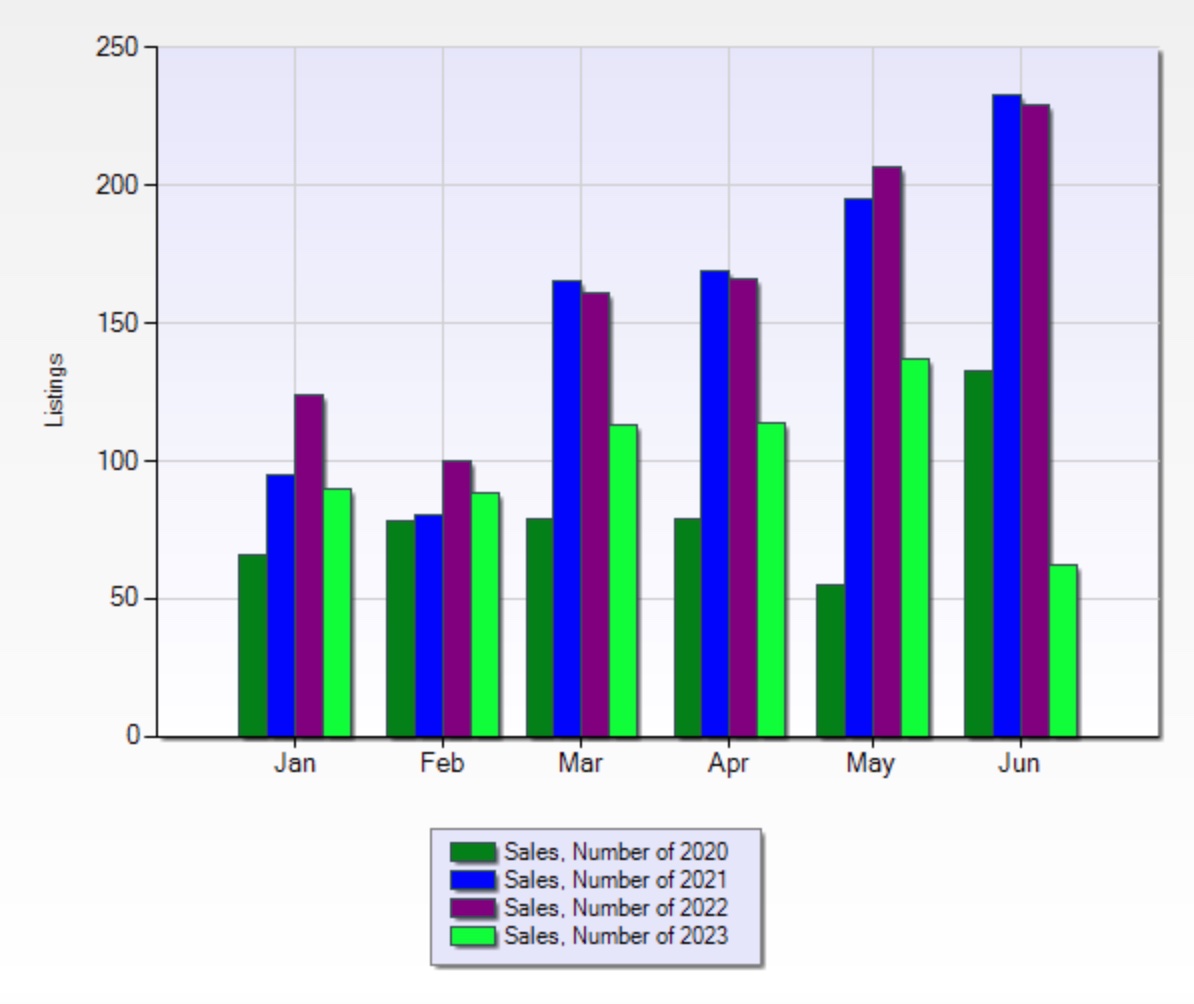
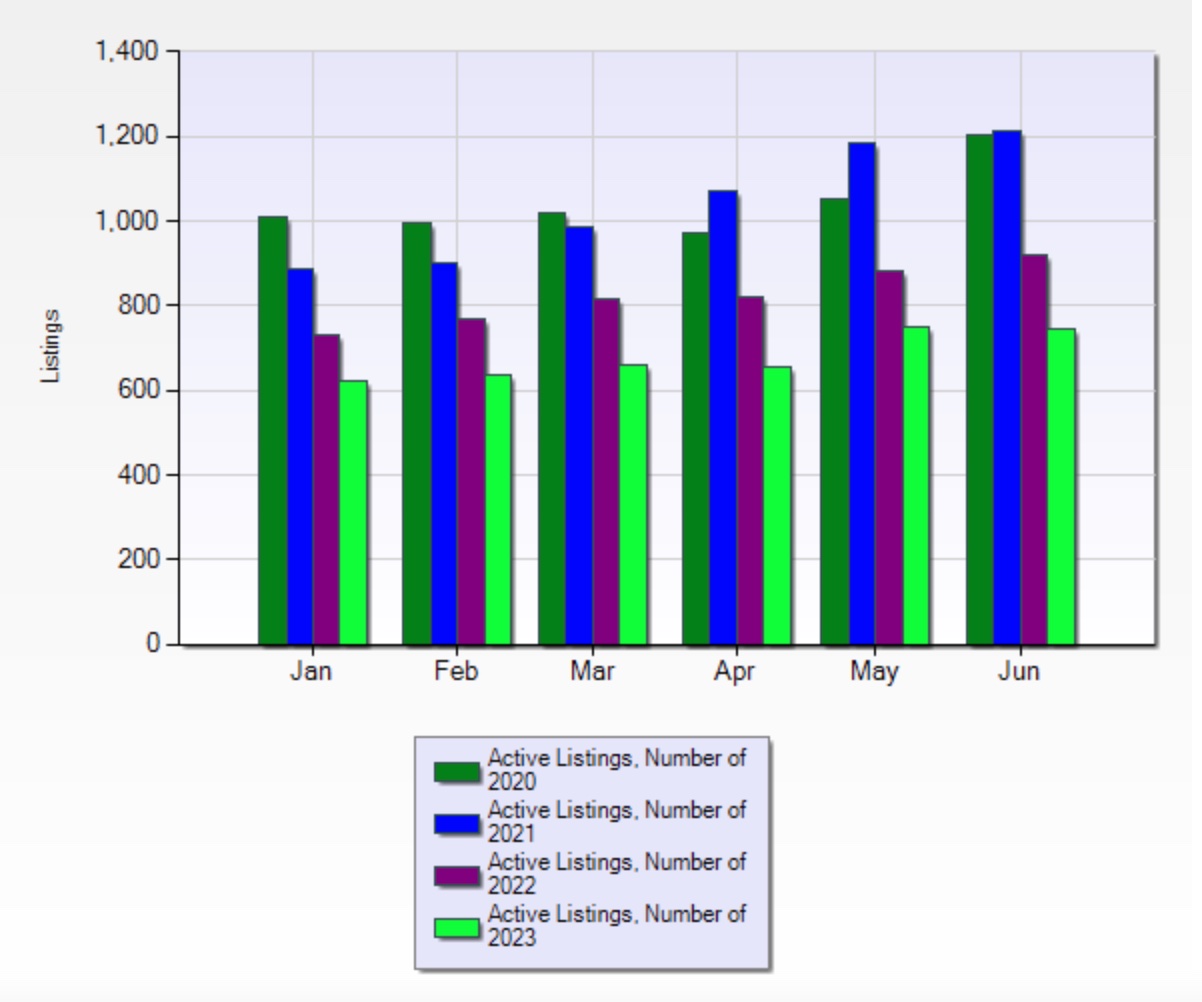
There’s a storyline that has been developing in the local real estate market over the past few years that is centred around the basic economic principles of supply and demand. Canada's housing crisis refers to the growing affordability and availability challenges facing homebuyers and renters across the country. While much of the national conversation focuses on major metropolitan areas like Toronto and Vancouver, smaller markets like St. John’s, Newfoundland, are not immune to these pressures.
In St. John’s, the housing market has historically been more affordable compared to the rest of Canada. However, recent trends—such as rising home prices, low housing inventory, and increased demand—have put pressure on buyers and renters alike. Factors like population growth, higher construction costs, and limited new housing developments contribute to these challenges. Join me in taking a closer look at what this currently looks like in the St. John’s real estate market, while I offer some opinions on what is likely to occur in the short to medium term with implications for how you decide to manage your real estate in the years to come no matter what your background.
Demand Side
Immigration First, immigration to Newfoundland and Labrador has seen a notable increase over the past decade. In 2015, the province had approximately 1,100 immigrants. Between July 1, 2022, and June 30, 2023, the province welcomed 5,337 new immigrants, nearly doubling the 2,841 newcomers from the previous year. This upward trend reflects the province's efforts to attract and retain newcomers through various initiatives and programs.The Government of Newfoundland and Labrador actively promotes immigration to address demographic challenges and support economic growth. Initiatives like the Priority Skills Newfoundland and Labrador program aim to attract highly educated and skilled individuals in sectors such as technology and ocean sciences. The people coming here are ready to work, make a living, and intend to buy homes.
While specific figures for Newfoundland and Labrador are lacking, national trends from Census data suggests exactly that - immigrants in Canada often prioritize homeownership and may employ various strategies, such as co-ownership with family members, to achieve this goal. And, anecdotally, it is clear in discussions with agents on the front lines of the home buying experience that new Canadians are very active buyers in the local housing market.
Diaspora of Retirement Age Newfoundlanders Then there are the stories of retirement age Newfoundlanders, triumphantly returning with cash falling out of their pockets due to selling in other robust, higher priced markets across the country. While comprehensive data on the return of retirement-age Newfoundlanders is limited, many agents have observed a trend suggesting that some individuals who left the province for employment opportunities are choosing to return upon retirement. Factors influencing this decision include a desire to reconnect with family, the appeal of Newfoundland and Labrador's natural beauty, and the lower cost of living compared to other Canadian regions.
The province has experienced significant out-migration, particularly during economic downturns such as the cod fishery collapse in the 1990s. However, recent trends indicate a positive net migration, with a record high of approximately 9,580 people in 2023. This shift suggests that more individuals, potentially including retirees, are moving to Newfoundland and Labrador. Community initiatives, like the "Come Home Year" events, encourage former residents to return and celebrate their heritage. For instance, in 2022, the province organized "Come Home 2022" to invite former residents back, which may have influenced some retirees' decisions to resettle in their home communities. While specific statistics on returning retirees are scarce, these initiatives and trends suggest a growing interest among former residents, including those of retirement age, in returning to Newfoundland and Labrador after years spent elsewhere.
Influx of Investment Dollars From Other Canadian Markets Many investors from larger Canadian markets are capitalizing on significant appreciation in cities like Toronto, Vancouver, and Calgary by cashing out equity or selling properties at peak values, then redirecting those funds into St. John’s real estate. With lower entry costs and strong rental demand, St. John’s provides an opportunity to reinvest capital at a higher yield while reducing overall risk exposure. Investors who’ve seen substantial gains in hot markets are finding they can purchase multiple properties in St. John’s for the price of a single condo in major cities, allowing them to build a more diversified portfolio. Additionally, lower property taxes and operating costs further enhance profitability, making St. John’s an increasingly attractive destination for those looking to stretch their investment dollars while still benefiting from a stable and growing real estate market.
On the Supply Side
Active Listings & Average Sale Price Addressing raw data directly from the MLS, the numbers indicate a post Covid era drop that has not bounced back yet, as a result of a combination of economic factors mentioned in this post’s introduction. Quantifying the outcome, the St. John’s residential supply has taken an approximately 45% drop from the 10 year high of 15,752 listings, to around 9000 listings per year in 2023 & 2024.
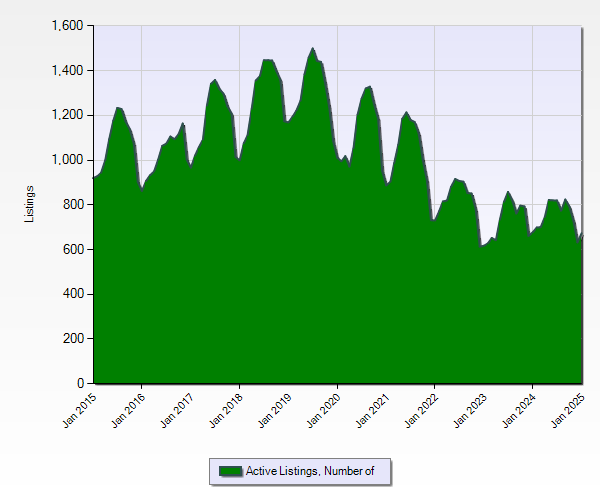
Boomer Housing While not the reason for the drop, I believe boomers hold one of the key solutions to the demand issue. In St. John’s, one of the most significant demographic groups shaping our housing landscape, job market, and overall economy is the baby boomer generation, which makes up approximately 20% of the local population. Point2Homes, an online real estate marketplace, reports that there are 49,255 households in the local housing market, and that 13,348 (27.1%) of those homes are primarily maintained by someone 65 years or older.
These homeowners, many of whom have lived in their properties for decades, are creating unique challenges—and opportunities—for the market. Many boomers in St. John’s own homes that were designed and decorated to their personal tastes years ago. While these homes may hold sentimental value and are perfectly functional for the owners, they’re often considered “dated” by today’s buyers. As a result, these homes don’t command the high prices homeowners expect when compared to smaller, newer properties that fit today’s trends. The problem for buyers is that there are not a lot of options when it comes to newer modern homes either, so they are willing to buy older homes if they became available, but they simply are not.
The consideration for boomer generation homeowners is easy to understand: Why sell a home they love, only to struggle to find a suitable, smaller property in a market where supply is tight and competition is high? Especially when they are comfortable in a house that is often largely paid off and was custom built for their preferences. Instead, many choose to stay put in their larger homes, continuing to maintain the properties as best they can, for as long as they can. Until they simply cannot anymore - usually due to health conditions and general aging.
The Rental Option: A Growing Trend
Major developers and investors in St. John’s seem to have noticed this trend and are responding by building multi-family units. Data from the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation indicates that in the St. John's Census Metropolitan Area, multiple-unit housing starts totalled 323 units from January to December 2024, representing a significant 129.1% increase compared to the 141 units recorded during the same period in 2023.
Luxury rental developments like One Churchill Park, Star of the Sea Residences, Macpherson Suites, MIX Apartments, and Regency Towers are quickly becoming the go-to option for developers catering to the boomer market in St. John’s. As baby boomers look to downsize from traditional homeownership while maintaining a high standard of living, these upscale rental communities provide the perfect balance of comfort, convenience, and modern amenities. Offering features such as spacious layouts, high-end finishes, fitness facilities, social gathering spaces, and underground parking, these developments appeal to retirees and empty nesters seeking maintenance-free living without sacrificing quality or location.
KMK Capital is continuing the trend by planning another large apartment complex on the site of the former Max Athletics building in the east end. This upcoming project is expected to further solidify luxury rentals as a preferred housing option for boomers who want to enjoy a lock-and-leave lifestyle while staying within established, amenity-rich neighborhoods. With a shifting real estate landscape and increasing demand for premium rental accommodations, developers are strategically positioning these high-end apartment complexes to attract a demographic that values both luxury and long-term flexibility.
What Happens When Boomers Finally Sell?
Over the next 10-15 years, as boomers transition out of homeownership, we could see a significant wave of properties hitting the St. John’s market. At first glance, this might suggest an oversupply scenario, leading to downward pressure on prices. However, if demand remains strong—driven by solid economic planning, steady in-migration, and continued interest in the local real estate market—this generational shift could play out in a way that rewards early sellers rather than causing a broad price correction.
Those boomers who choose to list their homes sooner rather than later may benefit from the current supply shortage, where eager buyers are still competing for limited inventory. With pent-up demand already driving market activity, the first wave of sellers could see multiple offers and premium pricing, capitalizing on an environment where buyers have fewer choices. However, as more boomers list their homes in the years to come, the initial supply crunch could ease, reducing the urgency among buyers.
Boomers who wait too long may find themselves in a more balanced or even buyer-favored market, where the influx of similar properties provides more options and dampens competition. This shift wouldn’t necessarily crash prices, but it could mean longer selling times and the potential for softer negotiations. The key takeaway? Those looking to maximize their home’s value may want to act sooner rather than later while demand remains intense and supply remains constrained.
What Does This Mean for Buyers and Sellers?
If you’re a current homeowner or potential buyer in St. John’s, understanding this trend is key. Here’s how it could impact you:
1. For Boomers: If you’re considering selling your home, now might be a good time to plan your move while demand remains strong and supply is limited. Waiting too long could mean competing with a flood of similar listings in the future.
2. For Buyers: Keep an eye on how the market evolves. As boomers begin selling their homes in larger numbers, you may find more opportunities to purchase spacious, affordable properties—especially if the market shifts in your favour.
3. For Investors: The growing rental market could present opportunities for those looking to invest in multi-family developments or renovate dated homes to meet modern buyer expectations.
The Bottom Line
The boomer generation is shaping the St. John’s real estate market in ways that will continue to unfold over the next decade. As trends shift—whether through downsizing, transitioning to rentals, or an eventual increase in available homes—it’s essential to stay ahead of the curve. No matter where you find yourself in the market, I’m here to help you navigate the changing landscape, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your long-term goals. If you’re looking for guidance in this evolving market, let’s have a conversation—I’d be happy to help.